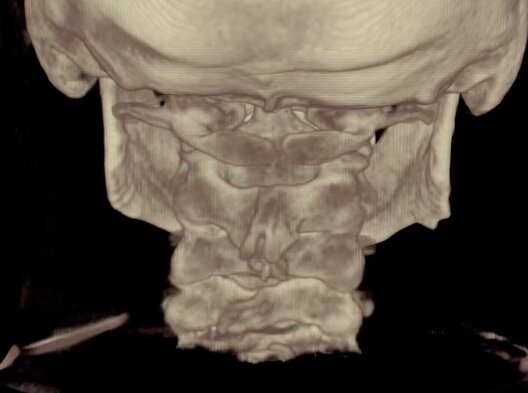
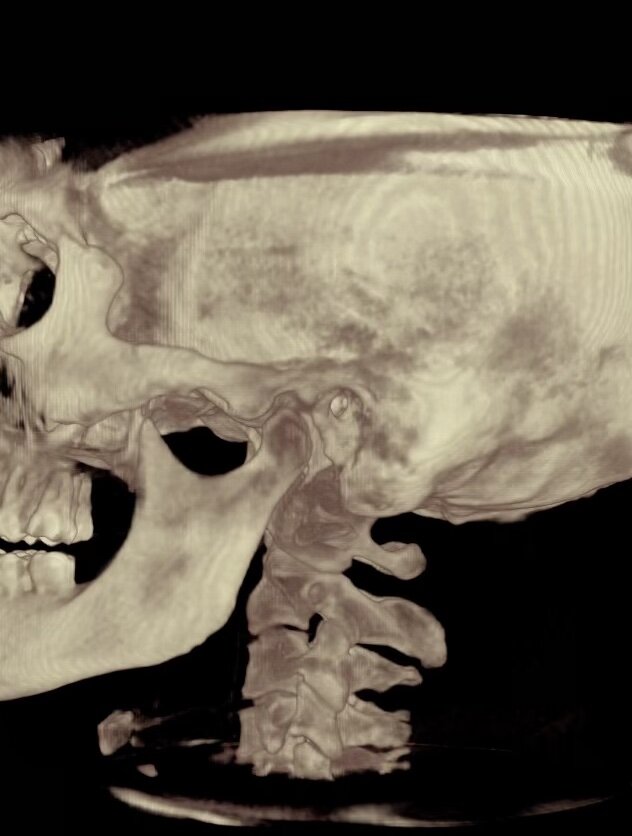
This is a Cone Beam CT scan.
It is slowly, but surely taking the place of regular X-rays.
The first thing I look at is this 3 dimensional view.
This gives me a good overview of what I am looking at and what to look for. I do my actual analysis on the 2-D views that you see on the right side of the screen. But this gives me some good overall information. I can look at the discs and the disc spaces, I can look at the holes between the bones where the nerves come out. I can look straight down from the brain through the cervical spine just to see what is going on there. So that's always what I start with first, just to get an overall view of what is going on.
Then I move to the 2-D views.
The first thing I do is I create these red lines that kind of square up the skull so I have some reference points. On this picture here, the head is pretty level, but on this picture here you can see there's quite a bit of tilt towards the right.
We want to look at the top joint in the spine where the skull sits on the top bone in the neck. Looking at the joints here on each side, and we'll take some measurements of it.
I'll just do a real quick version of it. We spend a bit more time. There's a bit more of a process to it when we are really analyzing something. It's about the same on both sides on this particular patient.
Then we're going to look at each side particularly.
So I want to look right down the outside edge of that joint there. We're going to see that over here. And we need to change the angle a little bit so we can see right down the joint. Alright, now it clears out. Looks pretty even there. The outside edge of the atlas and the outside edge of the occipital condyle, or the bottom of the skull. Let's take a look at the other side.
Overall this process takes about an hour.
Now if you look here, you can actually see a very small misalignment there. On this particular patient the atlas, or the bone underneath the skull, has moved a little bit to the left and forward of the actual skull itself and gotten stuck.
So we have to design an adjustment to slide the bone right back down there.
One of the tools that help us do that and again I would be a little more careful when I am actually analyzing it. We're going to look at what the angle is there so we know how to place our body in comparison to the patient to slide the bone back into place without twisting and popping. There is a lot of other things that we analyze...